Yokohama has announced that it has successfully developed technology that enables AI to predict the physical properties of different rubber compounds.
The system has already been implemented into the company’s design process, and Yokohama envisages an acceleration of its compound development activities due to AI’s ability to carry out a large number of virtual experiments in a shorter timescale. Alongside this, Yokohama predicts it will also see a reduction in development costs, with the system also enabling less-experienced engineers to create new rubber compounds.
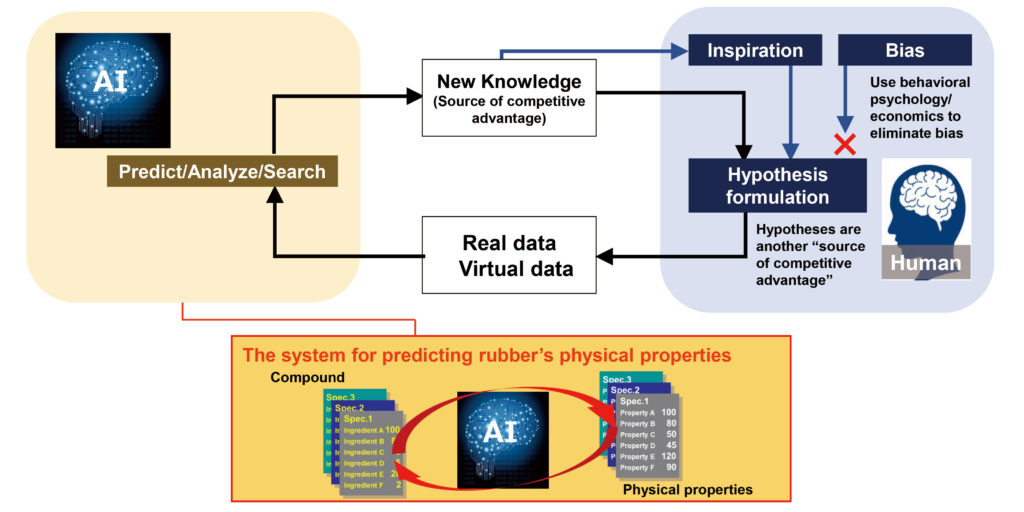
According to the company, the system works based on rubber compound design parameters input by an engineer, with the AI system forecasting the resulting compound’s physical properties. To help engineers confirm these predicted results, the system also displays the certainty of any predicted properties while also suggesting a compound composition closest to the initial target.
The technology has been developed under Yokohama’s HAICoLab (Humans and AI ColLaborate) concept, a project established to merge the potential of human innovation with the big data processing capabilities of AI. Launched in October 2020, HAICoLab aims to acquire new knowledge by creating and collecting data based on hypothetical conditions set by humans, and then applying AI to predict, analyze and search for the optimal result. Yokohama notes that it has already been advancing technological developments using AI in its material and tire design and development processes. For example, in 2017 it unveiled a new rubber material development technology that applies materials informatics, and a tire design technology that applies informatics technology.