Sumitomo Rubber Industries has developed a new simulation technique, Tire Aerodynamic Simulation, which is used to minimize rolling resistance.
The company is designing a tire shape that optimizes aerodynamic performance to reduce the fuel (electricity) consumption of electric vehicles. It has developed an AI simulation to visualize the airflow around the tire of a running vehicle. Sumitomo expects the next-generation EV tire resulting from this work to be launched in 2027.
According to data from a paper titled Improvement of Practical Electric Consumption by Drag Reducing under Cross Wind, electric vehicles experience less energy loss from heat compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles; therefore, air resistance represents a larger share of energy loss electric vehicles. Approximately 20% to 25% of air resistance energy loss in a passenger car is related to the tires and for EVs; if air resistance and resistance are combined, about 34% to 37% of a vehicle’s energy loss is related to the tires.
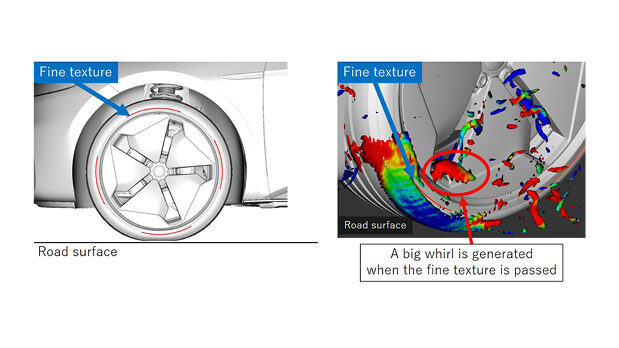
The Tire Aerodynamic Simulation technique adjusts tire patterns and sidewall textures to reduce air resistance. In comparison with the results of a wind tunnel experiment, which was conducted with an actual vehicle to confirm the accuracy of the simulation, the EV tire with a decreased airflow trend behind the tire and less unevenness on the sidewall showed lower air resistance values than the standard tire. Sumitomo suggests that this confirms the potential of the new simulation technique.